Genus/species (aliases): Candida zemplinina
Classification: Ascomycete; anamorph
Morphology:
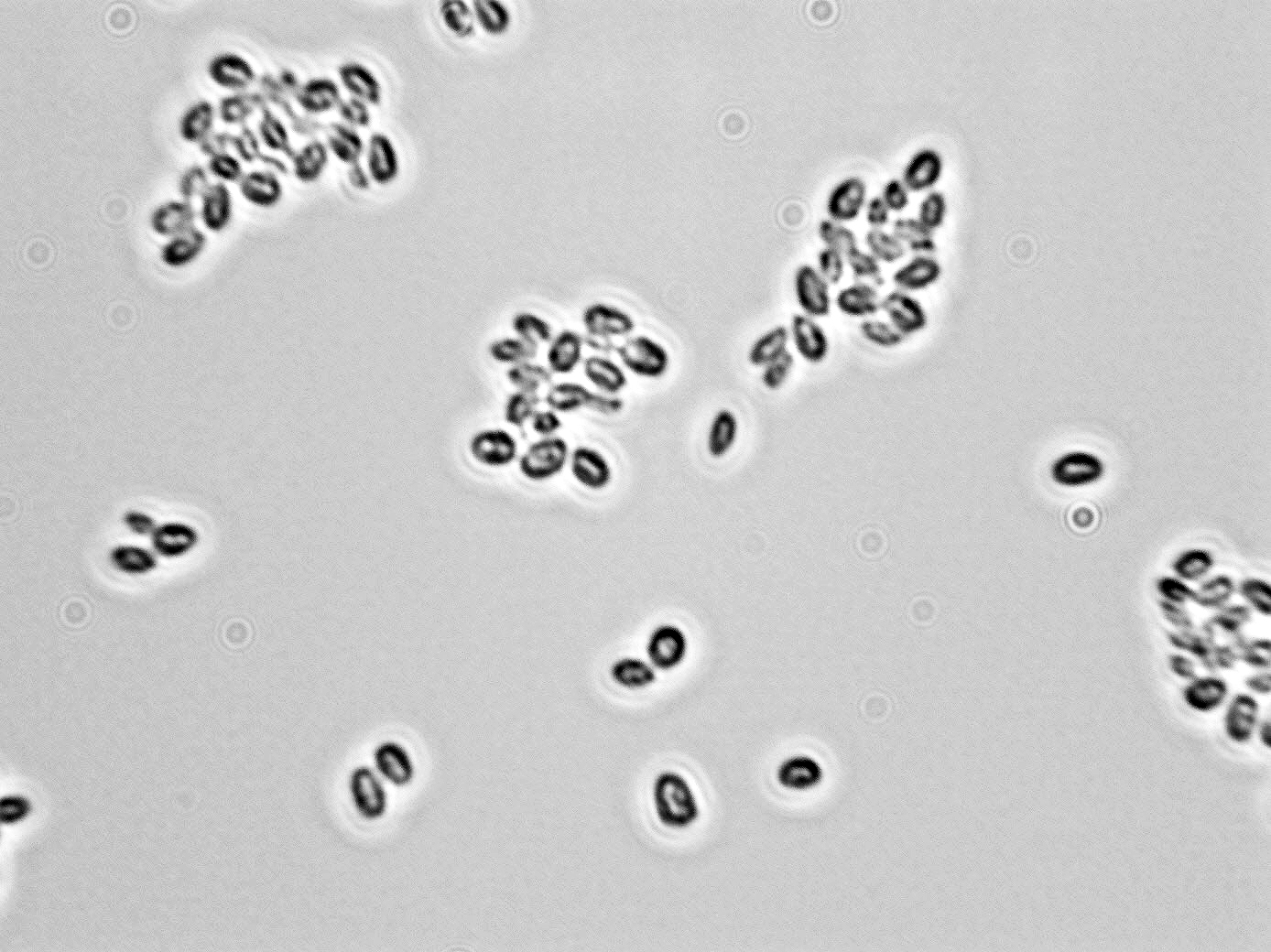
Cell: reproduces by budding; ellipsoid to elongated (2.2 – 3.0 x 3.0 – 5.2 μm) in single cells or pairs.
 |
 |
 |
 |
Colony:
- Malt agar: low circular with smooth to finely shaped margins and butyrous texture
- Spore: NA
- Zygote: NA
- Ascus: NA
Liquid Growth: pellicle film
Physiological Traits:
- Substrates:glucose, sucrose, raffinose, lysine, L-sorbose
- Products: ethanol, glycerol, acetaldehyde, acetoin
Ecological Traits: This organism is believed to be distinct to Tokaji, but has been isolated from California botrytized must (although 2 nucleotides differed in genomic analysis).
Distinguishing Features: It is almost indistinguishable from Candida stellata.However, by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis of 26s rDNA, there is a 8% difference in the D1/D2 domain.
Role in wine:
- Isolation from overripe and botryitized grapes has been accomplished due to the organism's tolerance to high sugar and low temperature conditions in which many other organisms cannot survive.
- This yeast can survive in both must and wine.Populations have been reported to be greatest in the beginning stages of fermentation, although, they are capable of completing alcoholic fermentation.
- It may be possible for this organism to exist during storage as other Candida species have can be present in barrels, producing a surface film.
Sensitivities:
- SO2:
- Sorbate:
- DMDC:
- pH:
- Acids:
- Ethanol:
- Anaerobiosis:
- Heat: X
