Genus/species: Lactobacillus brevis (Bacillus casei, Betabacterium breve, Lactobacterium breve)
Gram Stain: Positive
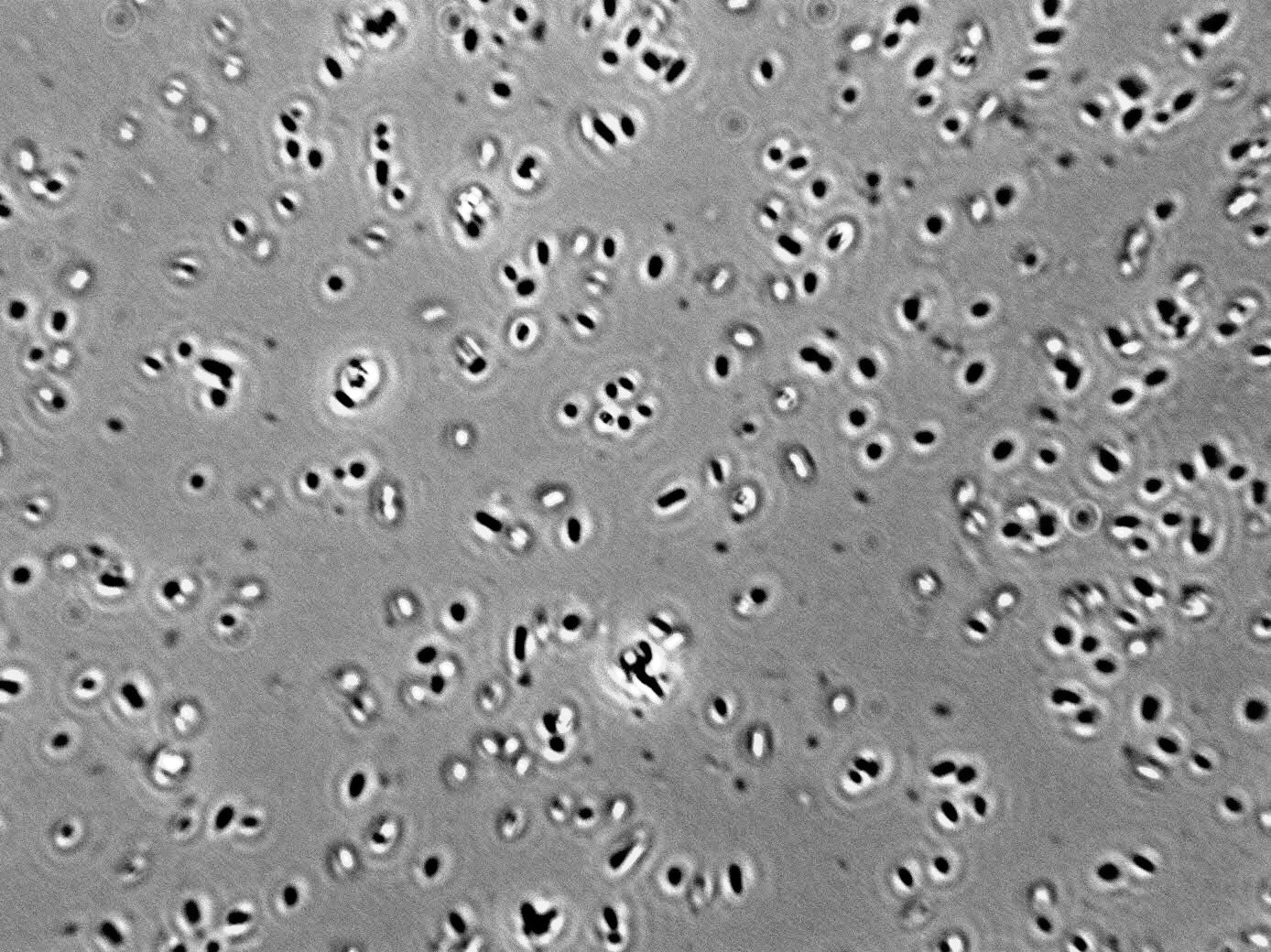 Morphology:
Morphology:
Cell:Rods with round ends, non motile heterofermentative 0.7-1μm x 2-4μm single or in short chains.
Colony: small colonies 2-5 mm, entire margins, convex smooth glistening and opaque without pigments
Liquid Growth: no pellicle is formed in liquid media
Physiological Traits:
Growth factor requirements; Calcium pantothenate, niacin, thiamine and folic acid as essential. Riboflavin, pyridoxal and vitamin B12 not required
Ecological Traits:
Normally isolated from milk, cheese, sauerkraut, sourdough, silage, cow manure, feces, mouth and intestinal in human and rats.
Distinguishing Features:
- Positive fermented carbohydrates; Arabinose, fructose, glucose, gluconate, maltose, melibiose, ribose
- Negative fermentation; Amygdalin, cellobiose, mannitol, mannose, melezitose, rhamnose, salicin, sorbitol, trehalose
- It can obtain NH3 from arginine
Role in wine:
Because of its tolerance to acetic media and high alcohol content it can grow on wine. Its heterofermentative pathway contributes to the consumption of pentose and formation of ethanol and other sub-products. It has a major influence on the MLF and sensory properties of the wine, as it can also use the organic acids as substrates. Often associated to mousiness in white wine fermentations.
Sensitivities:
- SO2:Tolerate low levels
- Sorbate: No growth
- DMDC: Not killed with 300 mg/L
- pH: 3-4
- Acids: Organic Acids
- Ethanol:20% v/v
- Anaerobiosis:
- Heat: No growth at 45 C
