Genus/species: Gluconacetobacter hansenii
Gram Stain: Gram negative
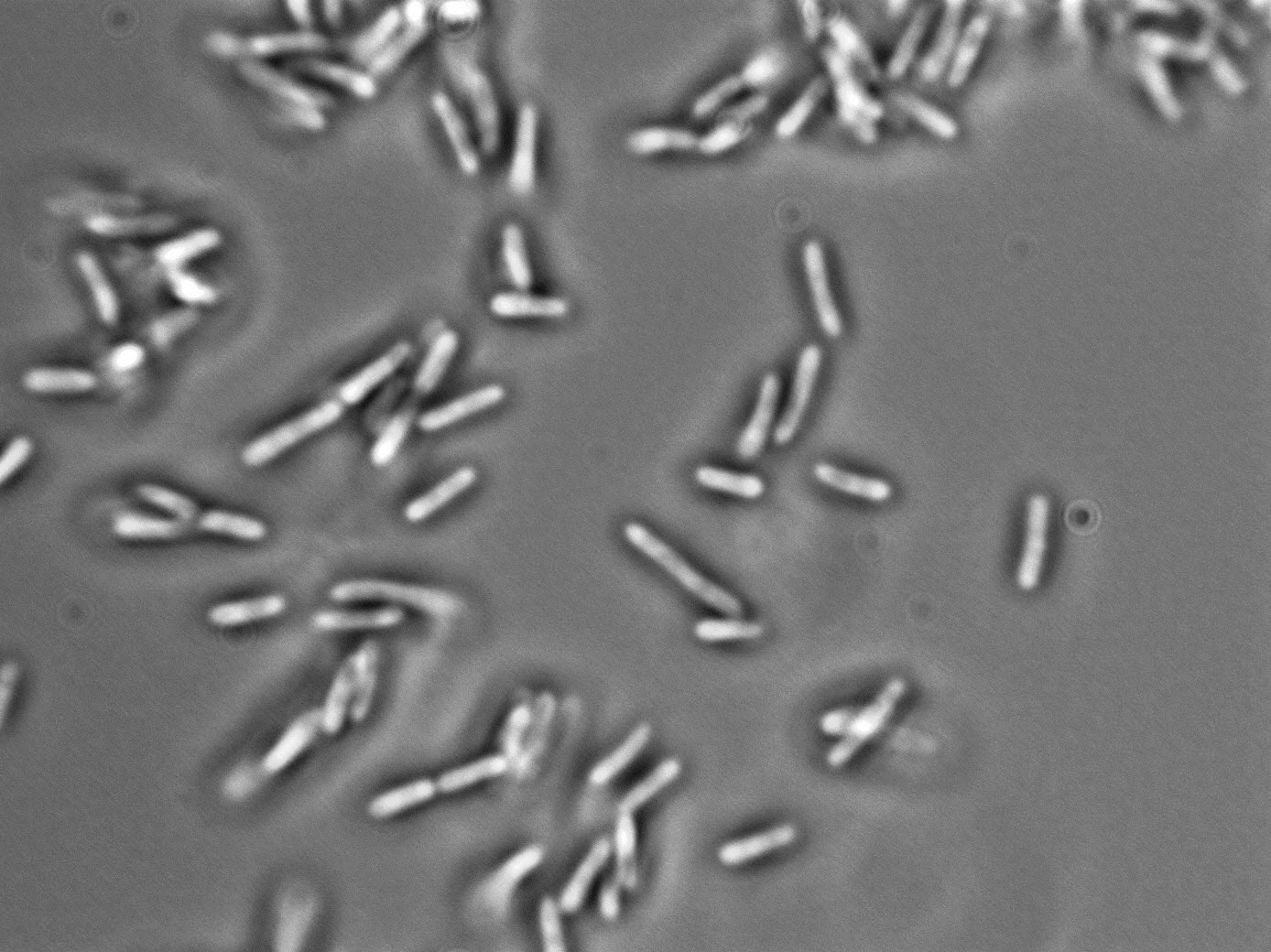
Morphology:
Cell: Rods, cell wall contains lipopolysaccharides
Colony:
- LG: Creates white/opaque colonies that are round, smooth and dry
- GYC: The bacteria converts ethanol into acetic acid which results in a clear instead of opaque substrate.
Liquid Growth: Produces, “rigid pellicle-type bacterial cellulose.” (Park et al. 2004)
 |
 |
Physiological Traits:
Aerobic bacteria found in high sugar environments. Carbon sources include sugar alcohols such as sorbitol, glycerol or mannitol and hexoses such as fructose and glucose. Gluconacetobacter does not have phospofructokinase and therefore cannot catalyze fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-diphosphate in glycolysis. It converts ethanol into acetic acid and produces organic acids. No essential amino acids are known for these bacteria.
Ecological Traits:
Found in substrates high in sugar such as rotten fruit.
Distinguishing Features:
- Acetic acid bacteria can be differentiated from lactic acid bacteria via the catalase test. The test would allow for rapid production of carbon dioxide bubbles, thus yielding a positive result.
- PCR can be used to distinguish between specific species in the Gluconacetobacter genus.
Role in wine:
These bacteria cause acetic acid production in wine which results in the production of vinegar. During fermentation, yeast cells usually dominate the growth and produce carbon dioxide which inhibits acetic acid bacteria. If yeast growth diminishes (nutrient deficiency, etc) then the bacteria can grow vigorously and dominate. This can result in a stuck fermentation.The metabolism of sugar can result in the creation of polysaccharides in wine which can later cause problems with filtering.
Sensitivities:
- SO2: Intolerant
- Sorbate: Tolerant
- DMDC: Unknown
- pH: Tolerance in some strains to wine pH 3-4.
- Acids: Tolerant
- Ethanol: some tolerant strains
- Anaerobiosis: Intolerant
- Heat: Intolerant
