Paper Chromatography for Monitoring Malolactic Fermentations
(Note: Chromatography reagent will stain your hands and clothes. Use gloves and a lab coat to avoid stains. Always wear splash goggles when working with chemicals)
1 Preparation of the chromatography solvent:
- 100 ml n-butanol (reagent grade)
- 100 ml water
- 10.7 ml formic acid (reagent grade)
- 15 ml indicator solution (1 g bromocresol green in 100 ml water)
- Mix chemicals and place in separatory funnel. Make sure stopper is securely closed. Mixture will separate into two layers; discard lower (aqueous) layer in proper waste container labeled “aqueous phase chromatography waste”
Store freshly made reagent in container labeled “new or rejuvenated chromatography reagent”.
2 Setting up chromatography paper (Figure 1):
- Clean bench top; place paper towels down on surface
- Take a sheet of chromatography paper and lay on towels
- Mark a pencil line across the bottom of the page, about 1 inch from the bottom
- Make tic marks at 2 cm intervals along the pencil line
- Label tic marks with standard or sample code using pencil
- Label sheet at top with initials, sample date and other information
- Only use pencil for labeling.
(Note: Sweat contains lactic acid. Handle only the edges of the paper with your fingers. You may want to wear gloves to avoid lactic acid contamination of your test.)
3 Spotting of chromatography paper:
- Use small (1.1-1.2 mm I.D.; 75 mm length) glass capillary tubes, one for
each sample or standard
- Draw liquid from sample in to the capillary and touch capillary to paper
- Allow no more than a spot of 1 cm to form on paper
- Allow spot to dry
- Repeat spotting 4- 5 times
4 Running the Chromatogram
- After all spots are completely dry, curve paper into a cylinder
- Staple ends to hold cylinder together – do not overlap ends of paper
- Transfer 70 ml of new or rejuvenated solvent to jar (large mayonnaise type)
- Carefully insert cylinder (Figure 2) spot side down
- Close lid carefully
5 Development of the chromatogram:
- After approximately 4 to 6 hours at room temperature the solvent will have ascended the chromatography paper carrying the spots with it.
- Carefully remove chromatogram careful not to touch the wet portion
- Carefully tear away edges from the staples
- Hang chromatogram in a well-ventilated area (chemical hood) to dry
- Yellow spots on a blue-green background should be visible and indicate the position of the acids
- All chromatograms should have standards (solution of individual acids) spotted to identify position of the acids (Figure 3).
6 Cleaning up:
- Carefully pour chromatography reagent into storage container marked “used chromatography solvent” (Chromatography reagent may be reused, but must be separated in a separatory funnel and occasionally reacidified before each use.)
- Take the empty mayonnaise jar to the sink and rinse it thoroughly with warm water. The first rinse should go into a container labeled “acid waste”.
- Place the cleaned jar upside down on clean paper towels for the next person to use.
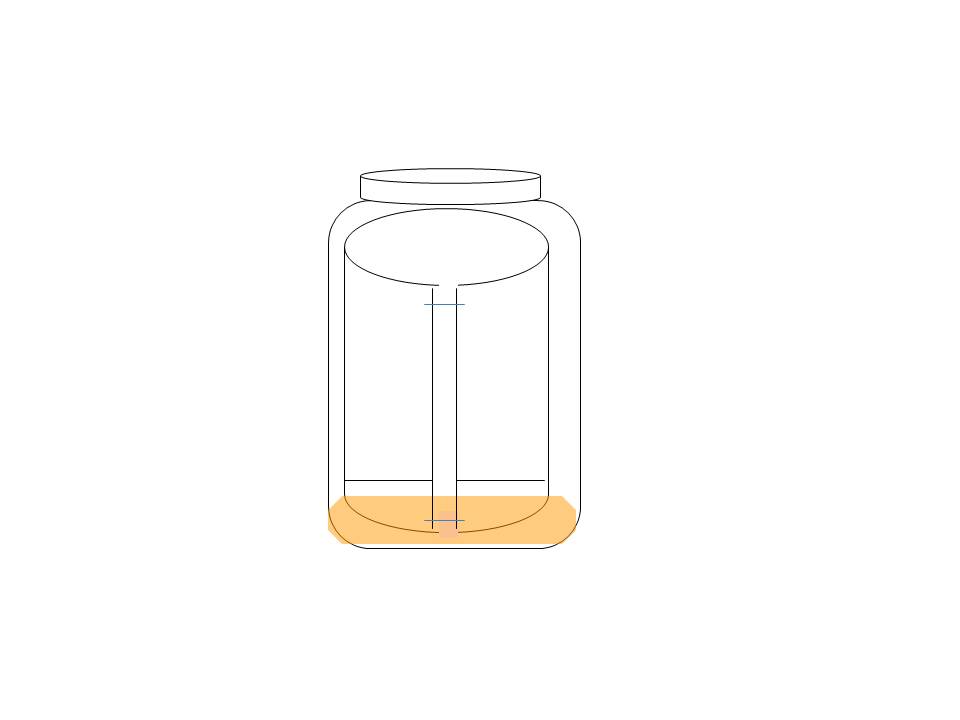

Figure 2: Paper Chromatography Jar Set Up
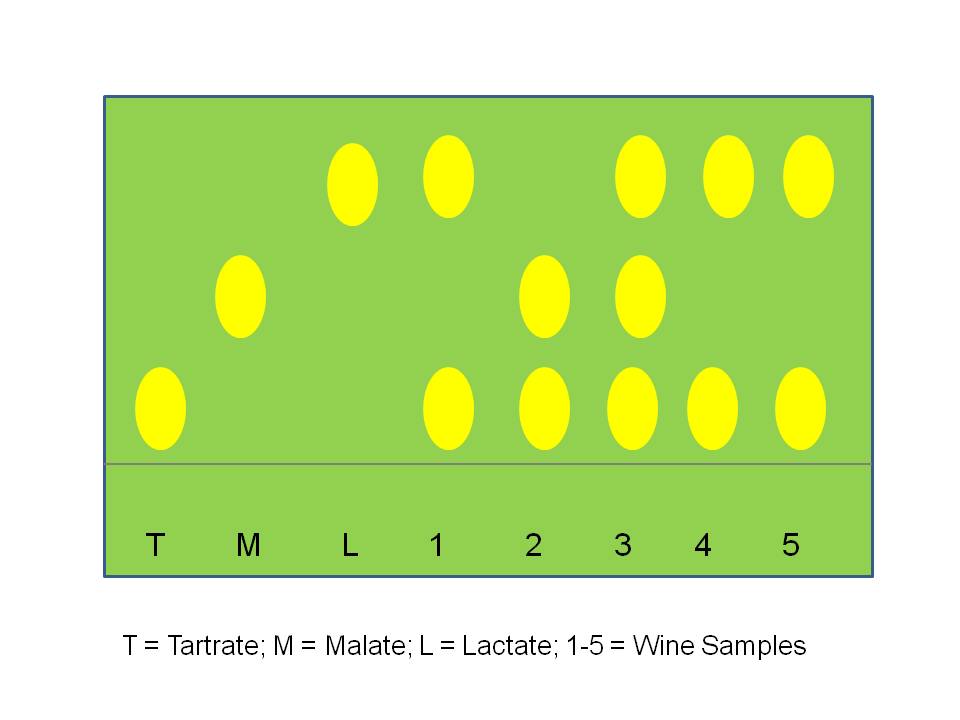
Figure 3: Paper Chromatography: Spot Location
Interpretation: Samples 1, 4, and 5 have completed the malolactic conversion; there is no detectable malate spot and the presence of lactic spots. Sample 2 has not started the malolactic conversion. Sample 3 may be mid-way through the malolactic conversion or the lactate may have derived from a different source.
